History of GraphQL
GraphQL was released in 2015 by Facebook. It has offered a new way and a promising alternative to the traditional REST API. Many companies including Github, Shopify, Intuit and many more have adopted GraphQL into their ecosystems. It's demand is increasing drastically and projected to grow exponentially over the new decade.
Note:- We will use an array as a database and will build API using Node.js with Appolo Server
What is GraphQL?

Demo from official graphQL website
As the name suggests, GraphQL is a query language for APIs. While SQL is a query language for managing relational databases, GraphQL is a query language that allows the client (frontend) to request data from an API.
Advantages of graphQL
Single endpoint :- In the traditional REST APIs, we have to create specific endpoints based on the data we want to request. This leads a problem of managing tens or hendreds or even more endpoints. GraphQL comes with a solution of having a single endpoint to query all the data.
Fewer server requests :- GraphQL allows us to make multiple queries and mutations with only one server request.
Specific data fetching :- Let's assume, we have a data of users with his id, name, address, contact, age etc. With the REST API, we cannot query only the id of a user but GraphQL only fetches what we actually need, and in this case we can get only id of the user with a single request.
Self-documenting :- GraphQL is self-documenting, meaning that all of our queries and mutations will automatically be documented by GraphQL.
Overall, it will save our time with a very few request, returning what actually we want.
Appolo Server
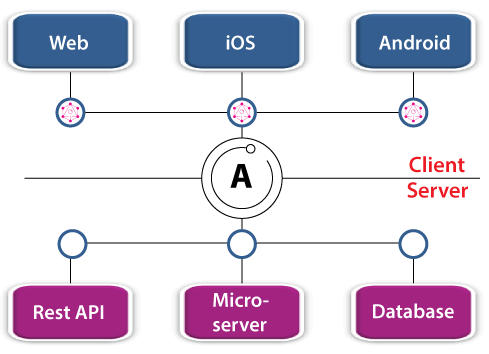
Since GraphQL is just a query language, we need a library that provides an easy-to-use GraphQL server. Luckily we have Appolo server which allows us for better scalability and features a larger community. Another GrpahQL server such as express-graphql also exists but Appolo server is in high demand due to its neat GraphQL interface for performing queries and mutation during development. We will learn in a while about query and mutation.
Building GraphQL API using node.js and Appolo server
Since we have explored much about GraphQL and Appolo Server, it's time to have some hands-on practise with some code.
Pre-requisites
You must have downloaded below mentioned things in your system
- Node.js
- Visual Studio Code - A code editor or any other code editor
You should have the knowledge of (or atleast familiar with)
- Node.js
- JavaScript
Steps for building API
Step 1 : Installing Dependencies / Package
- Create a folder with name such as
graphql-tutorialand open it with a code editor such asVisual Studio Code
We can do these things in our terminal with code given
mkdir graphql-tutorial cd graphql-tutorial- Initialize the directory with NPM
npm init -yThis will create a package.json file in your diredctory
Install the required dependencies
npm i apollo-server graphqlNote :
- apollo-server allows us to create a GraphQL server with ease
- graphql is the required dependency for apollo-server
- Create a folder with name such as
Step 2 : Running server initially
- Create an
index.jsfile in the root of your directory. Your directory should look like this :
- In
index.jsfile, write the below code to import ApolloServer and gql from apollo-server NPM module, we just downloaded.
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require("apollo-server")- Since GraphQL is a query language, we need to define our data with a schema(how our data will look like).
const typeDefs = gql` type Query { hello: String! id: Int! } `- Note :-
- Our typeDefs are passed into a gql tag. This tag sterilizes our type definitions and makes them readable to Apollo Server. This also allows for auto-completion during development.
- The Query type lists all the possible queries that can be performed by our server.
- hello and id are two different queries.
- We define the type of the returned value after a colon (:). In this case, hello returns a String type, and id returns an Integer type.
- An exclamation mark (!) after the type indicates a return value is required.
- Create an
Step 3 : Creating resolver function
- Now we need to tell our server what to return when a specific query is called and we can do this by resolver function. We will write resolver function for each and every Query that we defined in Query in typeDefs.
const resolvers = { Query : { hello : ()=>"Hello World!", id : ()=>Math.round(Math.random()*10) }, }- Note :
- The resolvers should match our typeDefs. Just like we had a Query type in our typeDefs, we have a Query object in our resolvers.
- The Query object contains the resolvers that correspond to our typeDefs. (Each query has a corresponding resolver function with the same name)
- Whatever you return in the resolver, the query returns to the client.
Step 4 : Creating server and Running it
- At first, we need to create an instance of ApolloServer and passing our typeDefs and resolvers in an object
const server = ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, }) server.listen({port : 8000}).then( ({url})=> console.log(`Server running at ${url}`) )- Now run the below code in your terminal
node index- Your
index.jsfile should look like this ```js
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require("apollo-server");
const typeDefs = gql
type Query { hello: String! id: Int! };const resolvers = { Query: { hello: () => "Hello world!", id: () => Math.round(Math.random() * 10), }, };
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers, });
server.listen({ port: 8080 }).then( ({ url }) => console.log(
GraphQL server running at ${url}) );- Visit *localhost:3000/* in your browser and you will find your server looking like this Step 5 : Querying our API
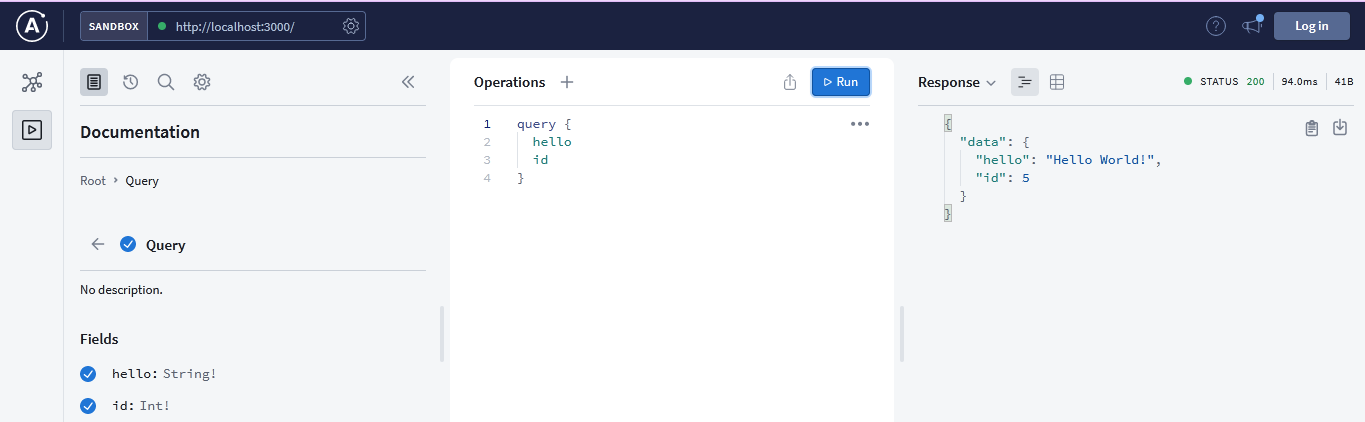
Now this is the time when we can query our API and for this we have a set-up of two query namely
helloandidwhich return Hello World! and a random number respectively.Write the code in query field which is present in operation tab or graphQL playground
query { hello id }Here is the result you will get as a response, when you click run button
The beauty of GraphQL can be seen here. If we remove id query, it will give response of the query hello only.
Conclusion
- We have successfully created a GraphQL API with node.js and appolo server with an ease.
- We are now familiar with the terms schema, resolver, query etc.
- We have learnt basics of GraphQL through this documentation, but for more advanced API you should visit here
Contributor :- Harsh Anand